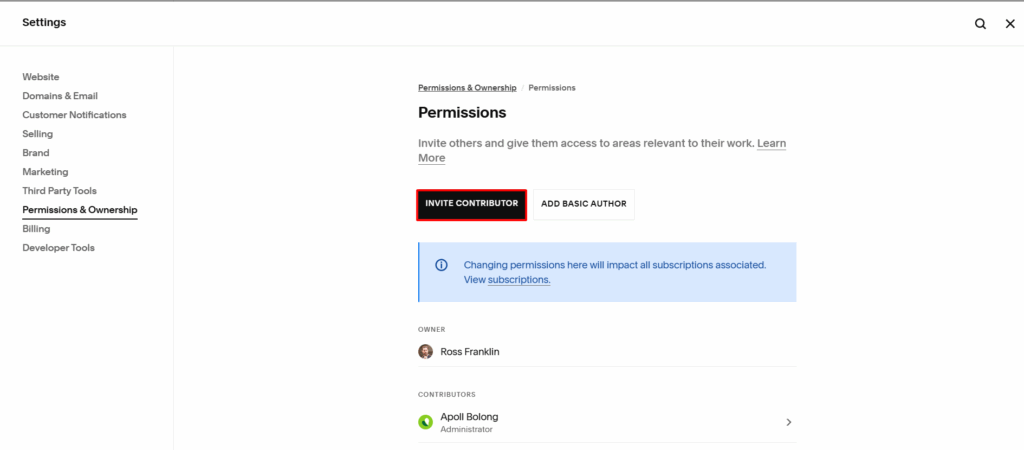
John Medina Buys Houses has been a trusted home-buying company in Los Angeles and Orange County for decades.
John, Brian, and Ricky have built their reputation by helping homeowners sell fast, avoid repairs, skip showings, and get a fair cash offer with integrity and compassion.
A few days ago, they reached out asking for help to understand why their rankings collapsed, why agencies kept letting them down, and what it would take to regain consistent, qualified seller leads.
What follows is a complete breakdown of their current SEO situation, what caused their traffic to disappear, how Google evaluates local service businesses today, and how AI agents can finally give their team full control without ever depending on another agency again.
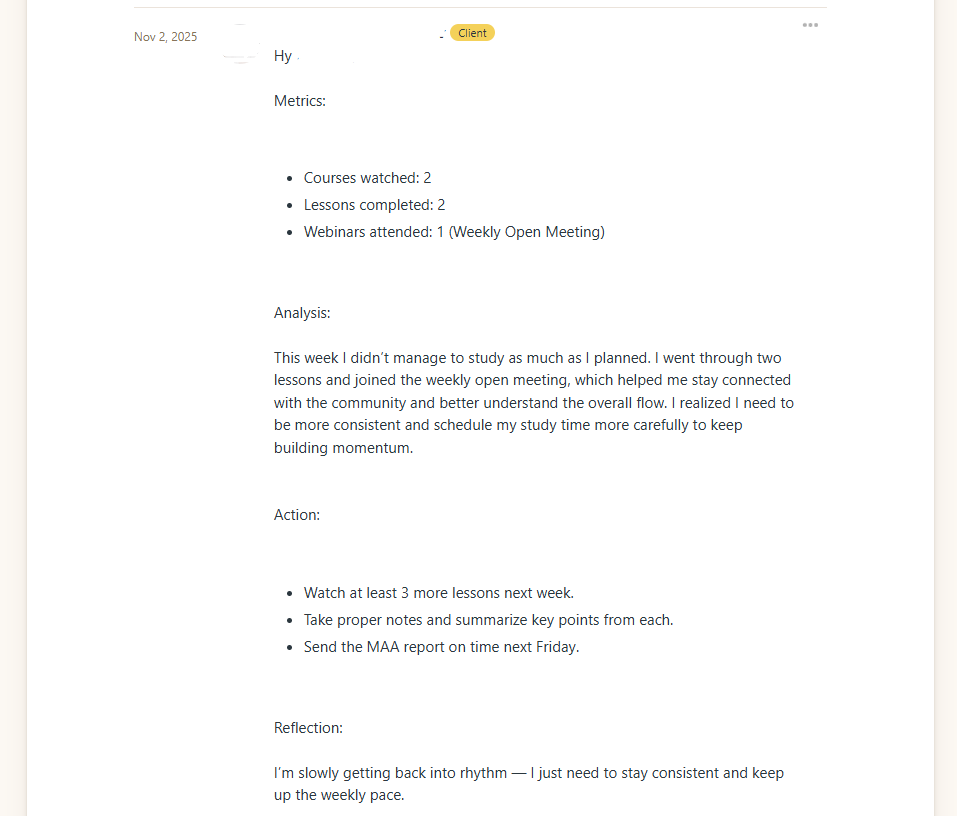
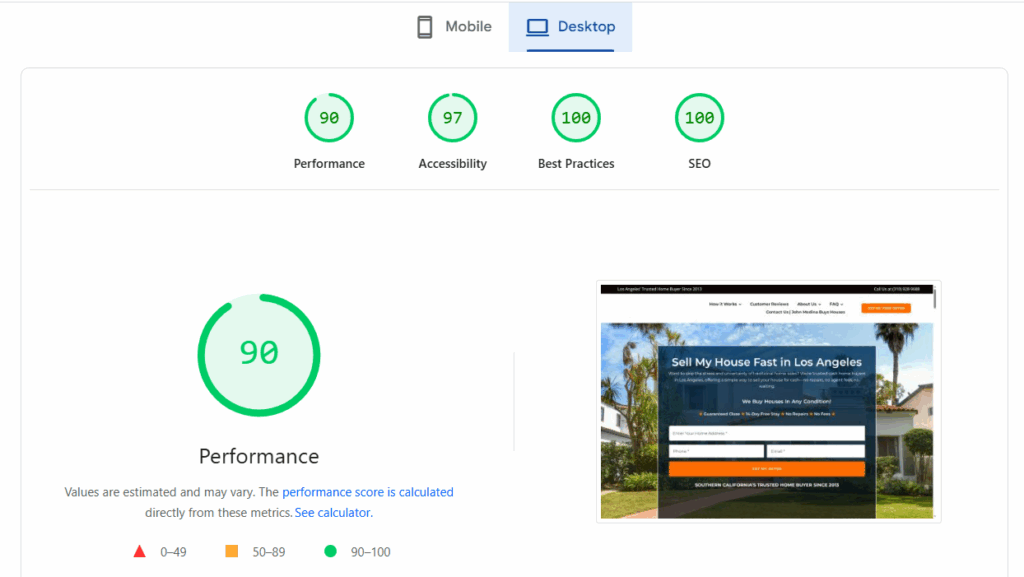
Before making any changes, we ran a full AI-powered audit designed to be rerun every month so progress can be measured objectively over time.
Audit snapshot date: Oct 31, 2025
What Happened to Their SEO?
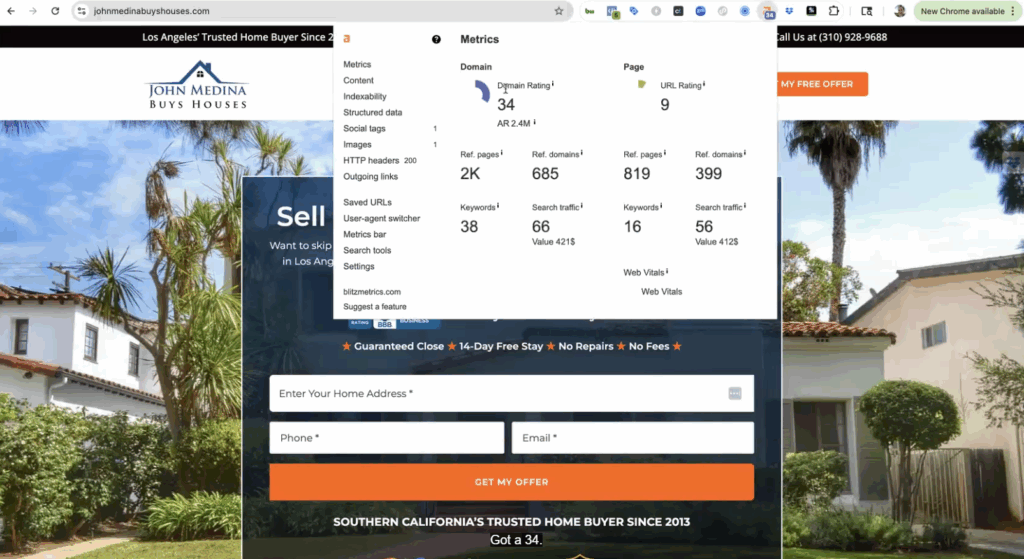
When we looked under the hood, the first thing we found was that the site still carries authority.
With a domain rating around 34, John Medina Buys Houses has more trust and history than most local real estate investors.
It has years of mentions, links, and brand equity behind it.
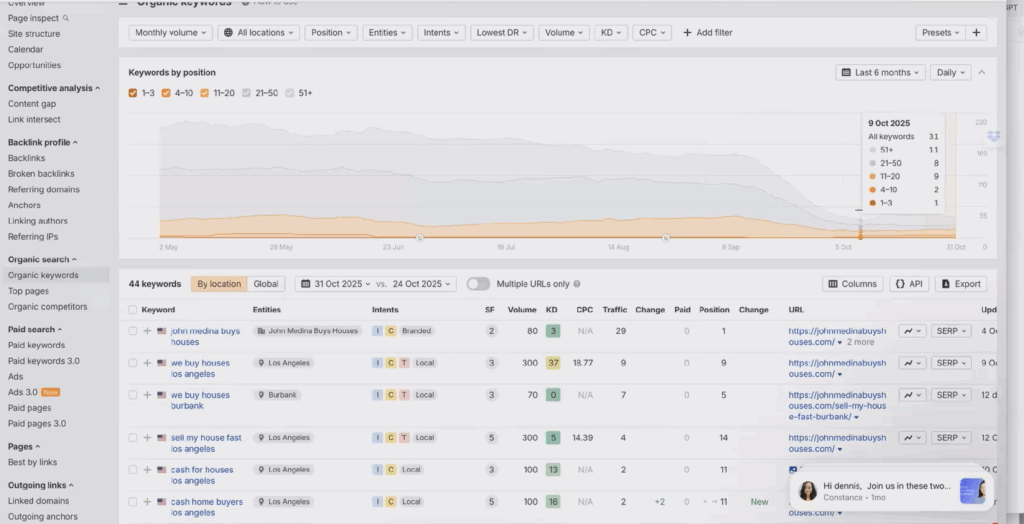
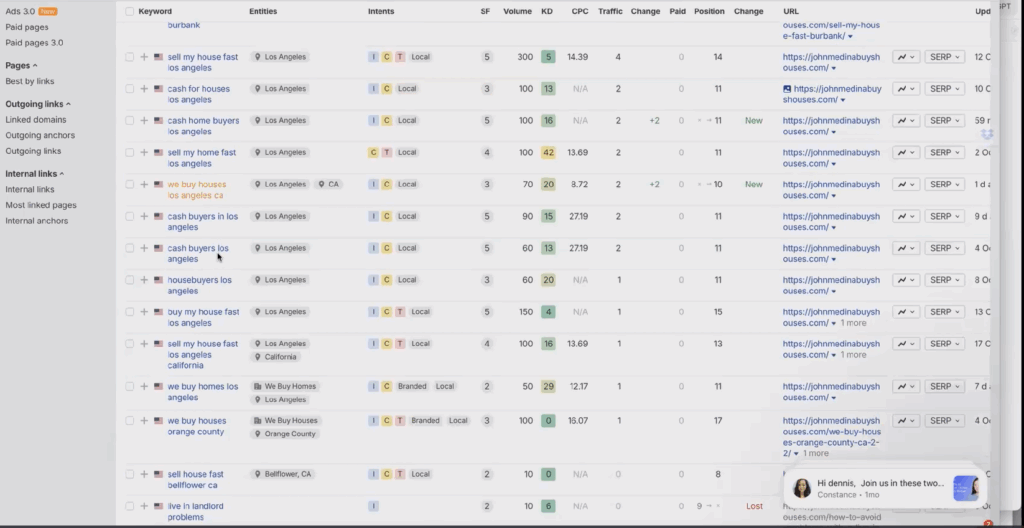
Yet despite this, the site only ranks on about forty keywords today.
Almost all of those come from the homepage.
Their city pages (Long Beach, Burbank, Compton, Englewood, Santa Ana, and others) are virtually invisible. The reason is simple.
These pages were created by previous vendors using the old playbook of keyword stuffing and templated content.
In the Burbank page alone, the city name appears over fifty times with no unique stories, photos, or meaningful information.
The Long Beach page repeats “Long Beach” more than seventy times while showing no real images from the area.
Google used to tolerate this. Today, those pages might as well not exist.
The algorithm has shifted heavily toward real-world proof that a business genuinely operates in the location it claims. And no amount of keyword repetition can replace that.
There’s also the website migration issue. The team moved off Carrot a couple of years ago, and the agency responsible created duplicate pages, wrong URL structures, canonical errors, and missing redirects. Rankings fell because the digital foundation was rebuilt incorrectly.
It was a structural collapse.
What Google Sees Today
Google evaluates local businesses using EEAT: experience, expertise, authority, and trust. Those letters sound abstract until you understand what they translate to.
Experience means photos and videos taken on actual properties in Long Beach, Burbank, Torrance, Gardena, and LA. It means showing up on camera. It means proving location through real footage, not stock photos.
Google’s AI can recognize landmarks, neighborhoods, street types, interior home conditions, and even whether an image is original or stolen.
Expertise comes from explaining the process of buying homes, talking through situations like inheritance or foreclosure, and showing that the team understands local real estate conditions. It shows up in videos, walkthroughs, and long-term documentation.
Authority reflects the BBB rating, the positive reviews, the years of history, the long-standing presence in San Pedro, and the body of work already in place.
Trust comes from consistency. One phone number. One address. One identity across GMB, the website, BBB, Linktree, YouTube, and citations.
Google saw the real-world reputation of the business. But digitally, the website didn’t mirror that reputation. Instead, it showed thin city pages, templated text, duplicated sections, and mismatched NAP information. The real John Medina Buys Houses is the opposite of that.
The GMB Profile and Local Signals
The Google Business Profile remains one of the strongest assets they have.
The business has real reviews, many of them detailed and heartfelt, and the BBB A+ rating helps reinforce their trustworthiness.
But the profile shows inconsistencies. Different phone numbers appear across different platforms, and the most recent reviews aren’t recent enough. Google heavily favors businesses that continue generating fresh, legitimate customer feedback.
The team has plenty of real images on the profile, which is excellent. But the website wasn’t using those images, opting instead for generic hero photos and automated text blocks. When a business has authentic content but doesn’t use it, that mismatch suppresses ranking potential.
Where the City Pages Went Wrong
Every city page followed the same pattern. The same hero image. The same structure. Nearly identical paragraphs, with the city name swapped in. No photos of the team in those cities. No stories about homeowners. No closings. No case studies. No references to local neighborhoods, houses, or community landmarks. And no embedded videos.
These pages look like they were produced by someone who had never been to California.
Google can tell. It rewards originality and penalizes sameness. A single real photo of John or Brian standing in front of a home in Long Beach is worth more than repeating “Long Beach” seventy times.
The business is missing documentation of its actual work.
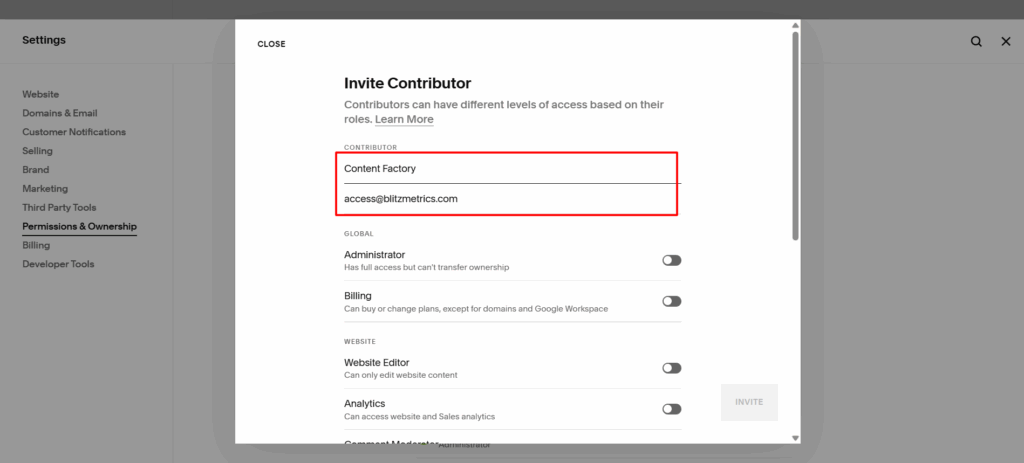
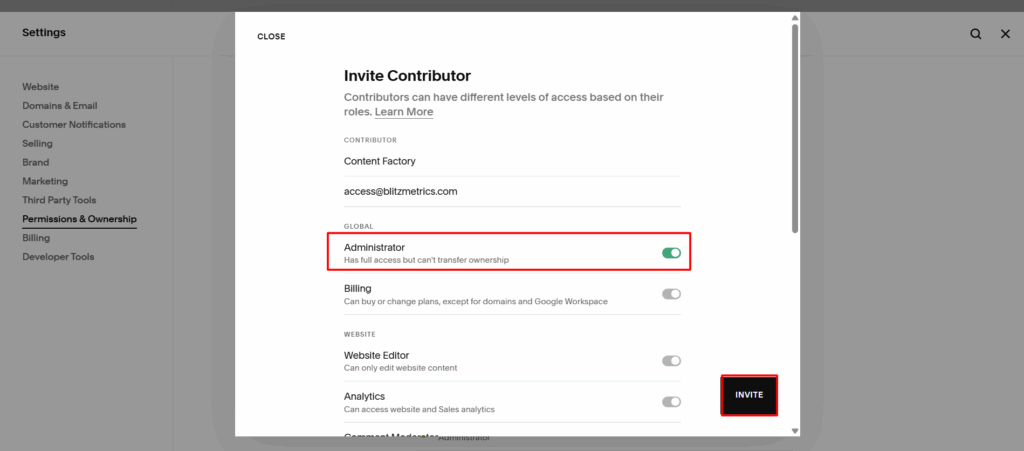
The Breakthrough: AI Agents Instead of Agencies
During our Zoom call, the team saw how ChatGPT Atlas agents work in real time. They are full execution engines that can rewrite entire pages, optimize metadata, insert images, build internal links, prepare city pages, edit YouTube descriptions, organize playlists, create article content, and even publish directly into WordPress.
Agencies have always been black boxes. They promise results, hide their processes, and deliver templated content that rarely moves the needle. AI agents eliminate that gap. You instruct them clearly, and they execute. If a step is ambiguous, they pause and wait for direction, just like a real team member.
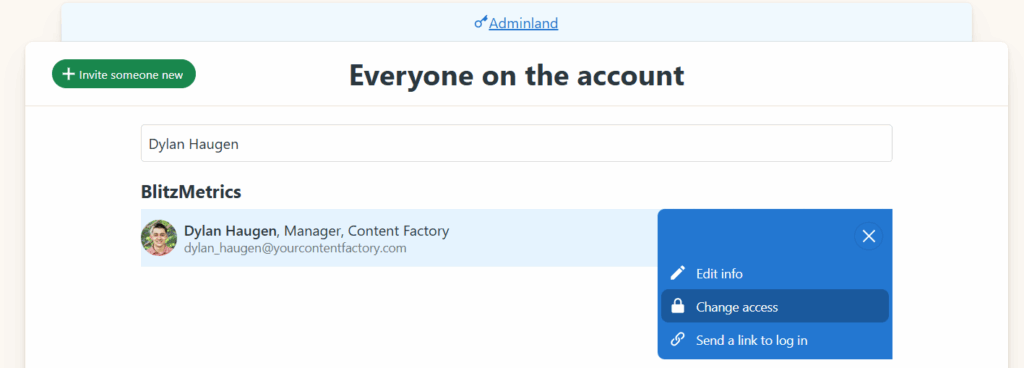
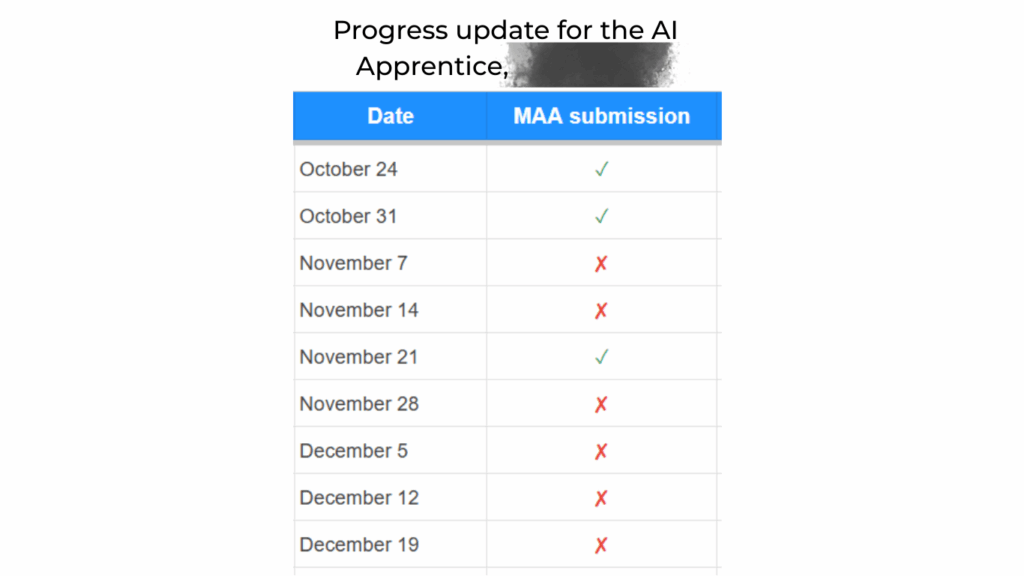
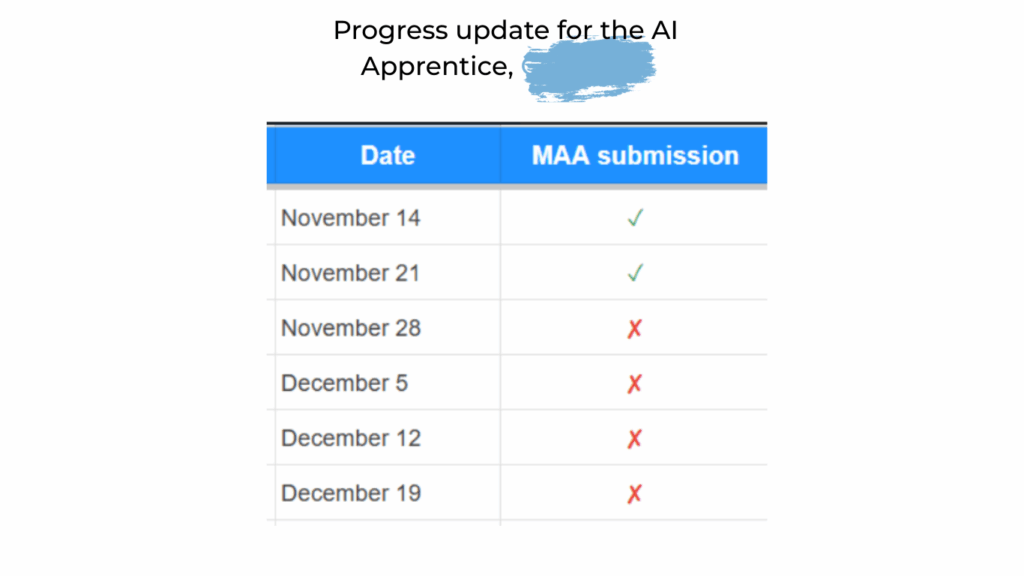
As part of this transition, one team member from John Medina Buys Houses has enrolled in our AI Apprentice program, ensuring the knowledge, execution, and systems stay inside the company instead of walking out the door with an agency.
This means the Medina team no longer needs a marketing agency. They simply need to manage their own digital workers.
Once trained, these agents can:
Write city pages with embedded photos.
Convert YouTube videos into blog posts.
Fix broken URL structures.
Rewrite all meta descriptions.
Analyze keywords.
Improve GMB posts.
Build ads.
Create remarketing audiences.
And repeat the process every day.
The digital work that once cost thousands per month becomes a daily routine executed in minutes.
What Needs To Happen Next
The first step is fixing identity. The business must use one phone number, one address, and one format across all platforms. Google needs to see a unified entity.
Next, the city pages must be rebuilt from scratch. Each one needs authentic photos taken in the area, a short story about a seller or situation from that city, a video where someone from the team speaks directly to the homeowner, and contextual information that only a local operator would know. The agents can assemble all of this once the raw ingredients are uploaded.
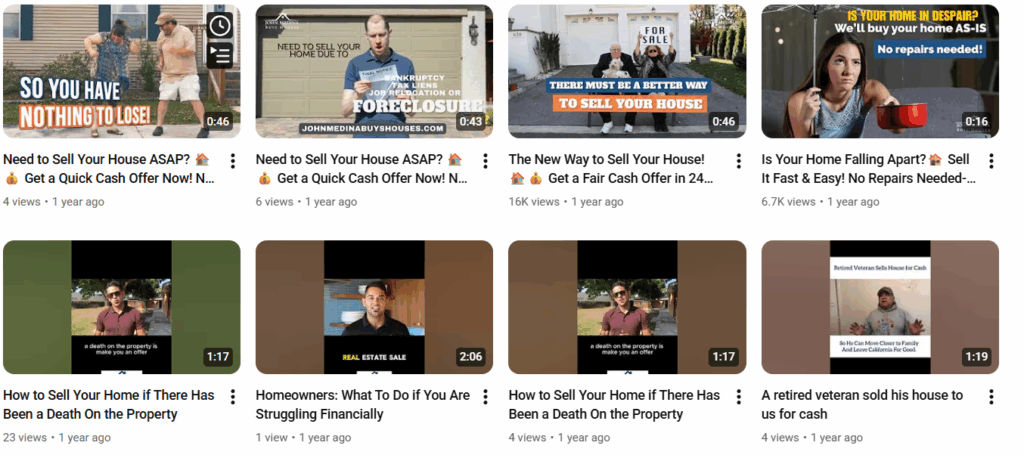
The 159 existing YouTube videos must be repurposed into articles, snippets, GBP posts, and playlists.
Most investors would kill to have that much content; John’s team already has it sitting untouched.
The site needs rewritten titles and descriptions. Schema should be added for reviews, FAQs, and the business profile.
GMB must receive fresh reviews every week, since this directly influences LSA performance.
And while SEO rebuilds its foundation, LSA and PPC should run immediately, since they generate phone calls right away.
Why the Team Is Actually in a Strong Position
Most investors struggle because they lack photos, reviews, videos, or history. John Medina Buys Houses has all of those in abundance. The business has been around longer than most competitors. The reviews are real. The videos are real. The team has been in every part of LA. They simply have not organized or published that experience.
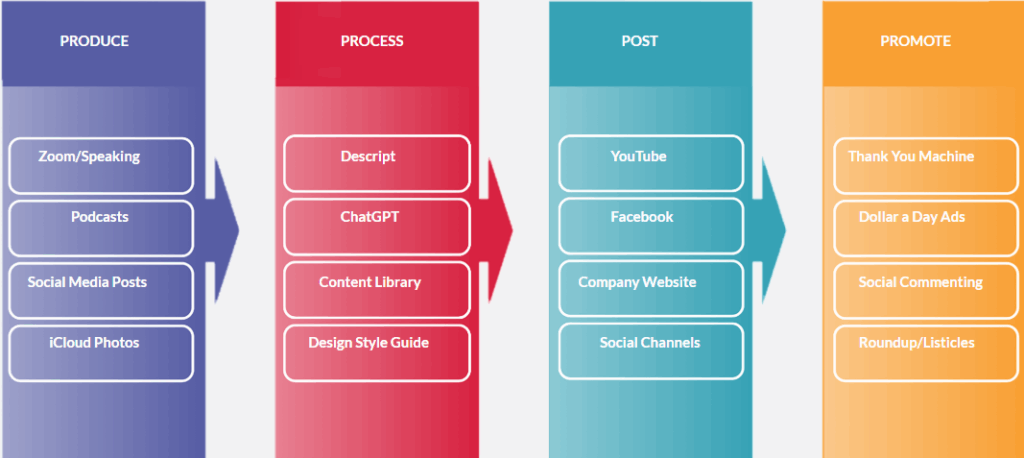
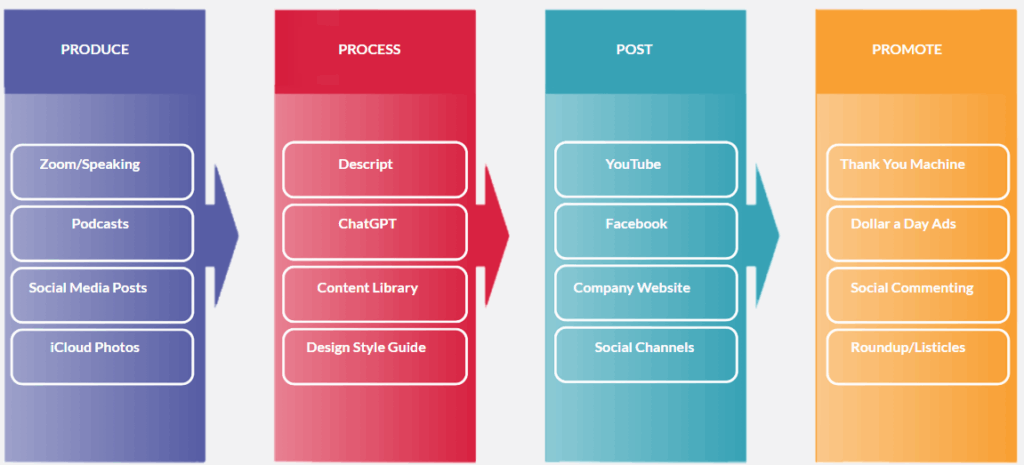
The fix is systematic. The four stages of the Content Factory (raw content, editing, posting, and amplification) make this inevitable once implemented.
The business has everything it needs to dominate again. It just needs the digital infrastructure to catch up with the real-world reputation they’ve built for decades.